A simple guide how to read engineering drawings
You don’t have to be an engineer to be able to read engineering drawings, while learning how to read engineering drawings can be a big advantage for you in your work.
What are engineering drawings used for?
Engineering drawings (also sometimes known as blueprints, manufacturing blueprints, prints, manufacturing prints, dimensional prints, drawings, mechanical drawings, and more) are a rich and specific outline that shows all the information and requirements needed to manufacture an item or product. It is more than simply a drawing, it is a graphical language that communicates ideas and information, explains MAKE UK.
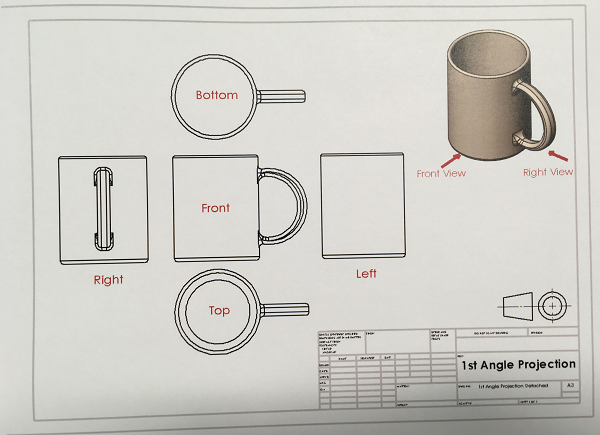
Why not just use a 3D model?
Unlike a 3D model, an engineering drawing offers a lot more specific information and requirements, including:
-Dimensions
-Geometry
-Tolerances
-Material type
-Finish
-Hardware
3D models are good to have and are usually (especially nowadays) used in conjunction with drawings. They are a good visual representation of the desired item, but do not contain all the information that drawings do.
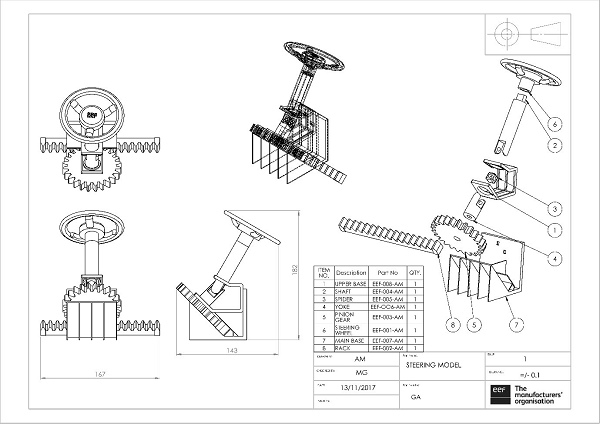
Information blocks
These blocks contain essential information about the assembly. They are usually located in the bottom right-hand corner of the drawing. These blocks provide details about what the drawing is for, for whom, part number and description, as well as information about the material and finish.
These are the main information blocks:
Title block
Start off by reading the title block found at the bottom right-hand corner of the drawing. There are other information blocks like it, but the title block serves as the context in which the drawing should be perceived.
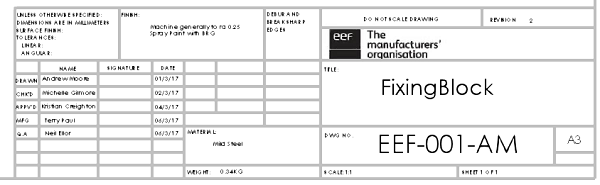
The title block contains information such as:
-Name and address of the company or agency who prepared or owns the drawing
-Part number and description
-Material
-Mass
-Finish
-General tolerances
-Projection details
-Scale used in the drawing
-Revision numbers
-Status of the drawing (Preliminary, Approved, etc.)
-Units used in the drawing
-Note that any information in the notes outside the title block that conflicts with the information in the title block should be considered as the right information and supersede the title block information.
Revision block
The revision block, located in the upper right hand corner, shows details about the changes that were made to roll the revision. The Revision Block includes the revision, the description of what changes were made, the date of the revision, and approval of the revision.
Bill of Materials (BOM) Block
Located usually either just above the title block or in the upper left-hand corner, the Bill of Materials block (also known as a BOM, Schedule or Parts List) contains a list of all the items and quantities that are required for the project or assembly. This is used for parts that either require assembly or when hardware should be added to the part.
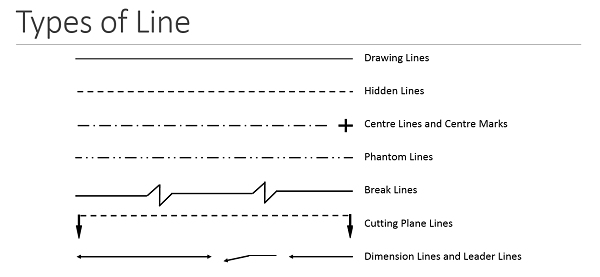
Lines
It is important to understand what each line type is and what they mean. There are three types of lines:
Visible line: Indicates an edge is visible in relevant view
Hidden line: Indicates the edge is behind a face
Phantom line: Mostly used to indicate an alternate position of a moving part. Also used to indicate a break when the nature of the object makes the use of the conventional type of break unfeasible.
Centre lines: drawn to indicate the exact geometric centre of the assembly. They are made from a series of lighter long and short dashes.